Numerical Aperture of Optical Fiber
Procedure
Procedure for simulator
Controls
- Start button: Starts the experiment.
- Switch on: Turns on the laser.
- Select Fiber: Selects the type of fiber used.
- Select Laser: Selects a different laser source.
- Detector distance (Z): Use the slider to vary the distance between the source and the detector (i.e., toward or away from the fiber).
- Detector distance(x): Use the slider to change the detector position (i.e., move left or right with respect to the fiber).
- Show Graph: Displays the graph.
- Reset: Resets the experimental setup.
Preliminary Adjustment
Drag and drop each apparatus in to the optical table as shown in the figure below.

- Then Click “Start” button.
- Switch On (now you can see a spot in the middle of the detector)
- After that select the Fiber and Laser for performing the experiment from the control options.
To perform the experiment
- Set the detector distance Z (say 4mm). We referred the distance as “d” in our calculation.
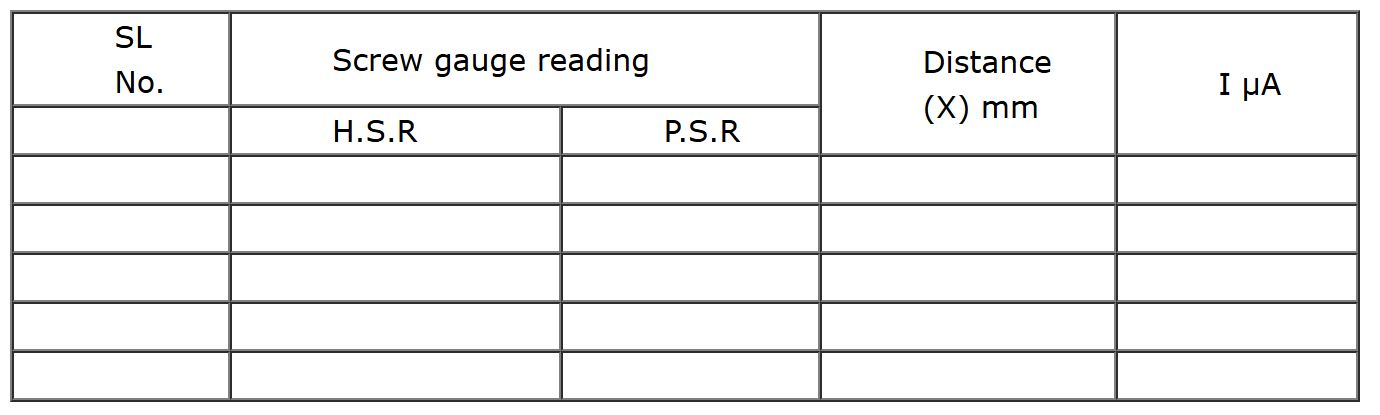
- Vary the detector distance X by an order of 0.5mm, using the screw gauge (use up and down arrow on the screw gauge to rotate it).
- Measure the detector reading from output unit and tabulate it.
- Plot the graph between X in x-axis and output reading in y-axis. See figure 5.
- Find the radius of the spot r, which is corresponding to Imax/2.71 (See the figure 5).
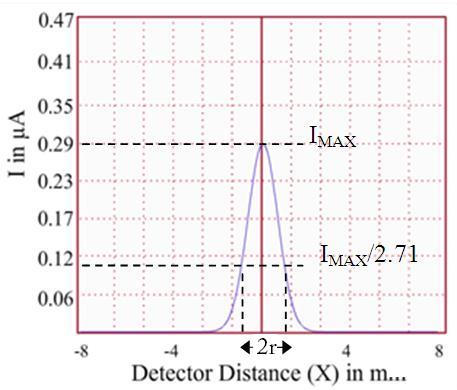
Figure 5
- Then find the numerical aperture of the optic fiber using the equation (4).
Observation column
Calculations
istance between the fiber and the detector, d = …………………………… m
Radius of the spot, r =……………………….. m
Numerical Aperture of the optic fiber, = .................
Acceptance angle, = ...............
Result
Numerical aperture of the optic fiber is = …………………
Angle of acceptance = ……………….
